Esketamine: What It Is, How It Works, and What You Need to Know
When standard antidepressants don’t work, esketamine, a nasal spray form of a ketamine derivative used to treat severe depression. Also known as Spravato, it’s one of the first new types of depression treatment in decades. Unlike SSRIs that take weeks to kick in, esketamine can lift mood in hours or days—especially for people who’ve tried multiple medications without success.
It’s not a first-line treatment. Doctors only prescribe it for treatment-resistant depression, a condition where at least two different antidepressants failed to help. Patients must take it under medical supervision because of potential side effects like dizziness, dissociation, or increased blood pressure. It’s given in a clinic, not at home, and you can’t drive for at least 24 hours after use. This isn’t a quick fix—it’s part of a structured plan that usually includes an oral antidepressant.
Esketamine works differently than older drugs. Instead of targeting serotonin, it affects glutamate, a brain chemical involved in learning and mood regulation. This is why it can help when other treatments fail. It’s also being studied for other conditions like PTSD and chronic pain, but right now, its only FDA-approved use is for depression that won’t budge.
People often confuse esketamine with recreational ketamine. While they’re chemically related, the medical version is purified, dosed precisely, and given in a controlled setting. Street ketamine carries unpredictable risks and no proven benefit for depression.
What you won’t find in most ads is how many people don’t respond to it at all. Studies show about half of users see meaningful improvement. For others, it’s a dead end—and that’s okay. The goal isn’t to make everyone feel perfect, but to give those stuck in deep depression a real shot at relief.
There are risks. Long-term use data is still limited. Some patients report bladder issues or cognitive changes after repeated doses. That’s why doctors monitor closely and avoid long-term use unless absolutely necessary. It’s not for people with a history of substance abuse, uncontrolled high blood pressure, or certain brain conditions.
Below, you’ll find real-world insights from posts that dig into how esketamine fits into broader medication safety, drug interactions, and mental health treatment. You’ll see how it compares to other options, what to watch for when combining it with other drugs, and why careful monitoring matters more than ever in today’s complex drug landscape.
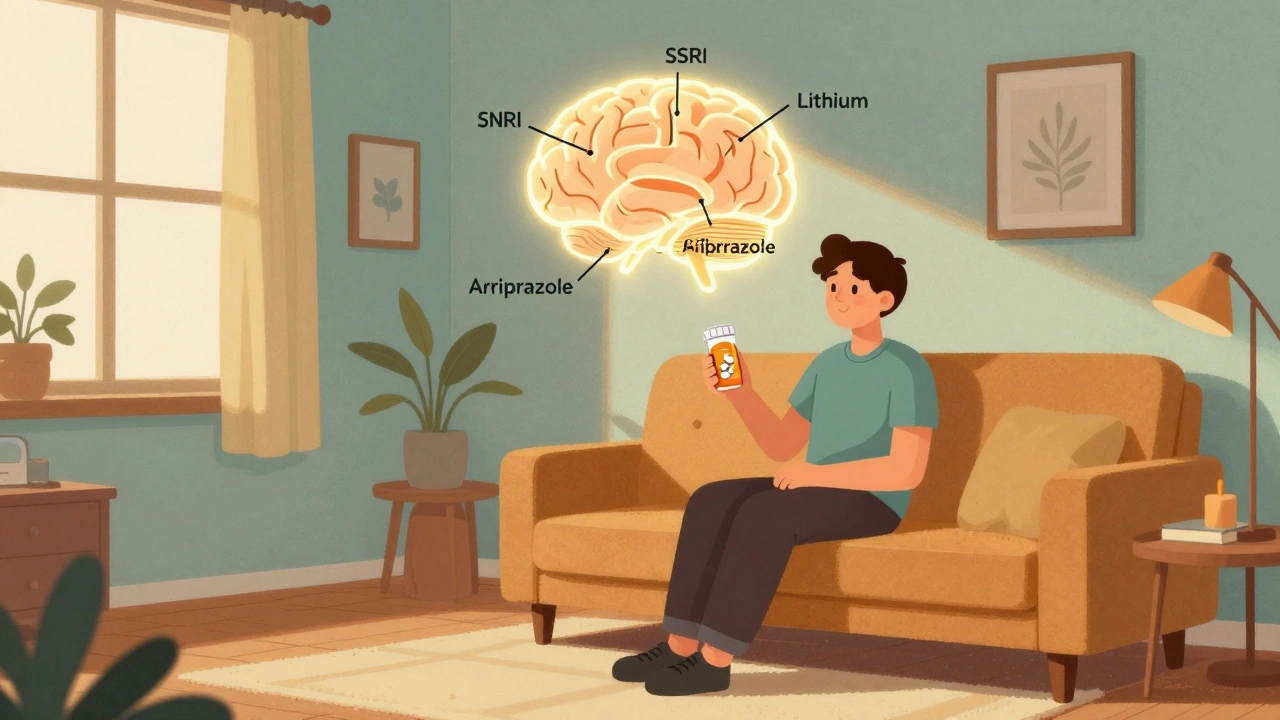
Treatment-Resistant Depression: Augmentation and Advanced Therapies That Actually Work
When antidepressants fail, treatment-resistant depression requires more than just switching pills. Learn about FDA-approved augmentations, rTMS, esketamine, and emerging therapies that actually work.
Read More