Bone Marrow Disorders – What You Need to Know
If you’ve heard doctors mention "bone marrow disorder," you might wonder what that really means. In simple terms, it’s any condition that stops the marrow from making healthy blood cells. The problem can show up as too few red cells (anemia), not enough white cells (risk of infection), or low platelets (easy bruising). Knowing the basics helps you catch warning signs early and get the right help.
Common Types of Bone Marrow Problems
There are a few big groups you’ll hear about. Aplastic anemia is when the marrow goes quiet and stops producing cells altogether. Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) involve faulty cell production that can turn into leukemia over time. Leukemia itself starts in the marrow, creating too many abnormal white cells. Finally, myeloproliferative neoplasms push the marrow to make too many red cells or platelets. Each type has its own quirks, but they all share the same core issue – disrupted blood cell formation.
How to Diagnose and Manage Them
The first step is a blood test. Doctors look at hemoglobin, white‑cell count, and platelet numbers. If something’s off, they’ll likely order a bone‑marrow biopsy – a quick needle sample that shows the marrow under a microscope. Imaging like MRI or CT can help if they need to see where the problem spreads.
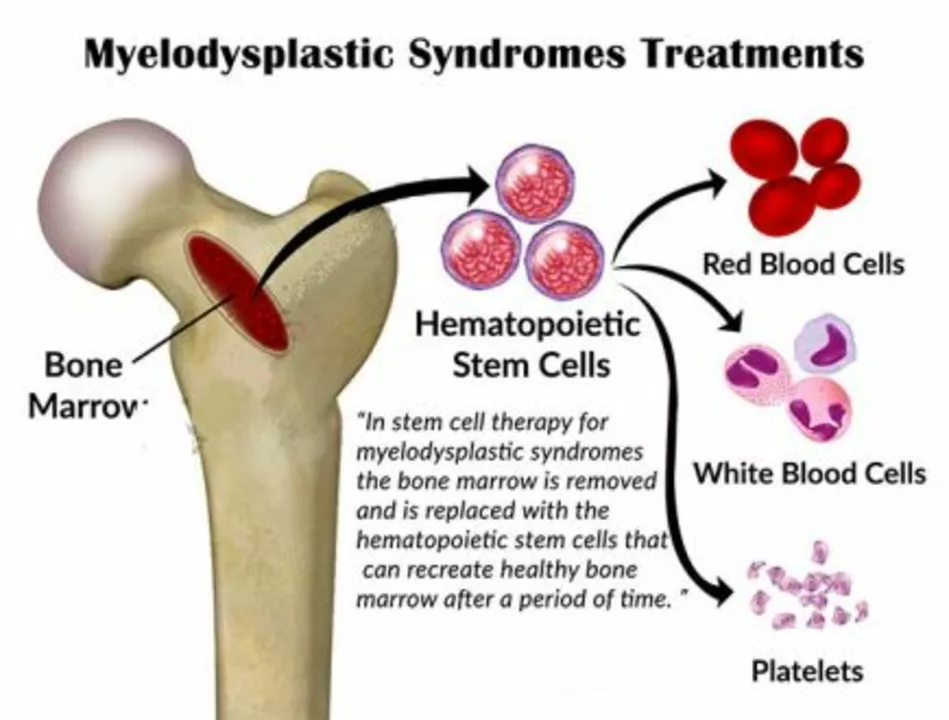
Once you have a diagnosis, treatment depends on the specific disorder and how severe it is. Mild cases might just need regular monitoring and vitamins. For aplastic anemia, immunosuppressive drugs or a bone‑marrow transplant are common options. MDS patients often receive growth‑factor injections to boost blood cell production, while some qualify for low‑dose chemotherapy. Leukemia treatment usually combines chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and sometimes transplant.
Beyond medication, lifestyle tweaks make a big difference. Eating iron‑rich foods (like spinach or lean meat) supports red‑cell health, while staying hydrated helps your blood flow smoothly. If you’re prone to infections, wash hands often and avoid crowds during flu season. Regular exercise improves circulation and keeps your immune system active, but talk to your doctor before starting a new routine.
Living with a bone marrow disorder can feel overwhelming, but knowing what’s happening inside your body gives you power. Keep track of symptoms – fatigue, easy bruising, frequent infections – and report changes right away. Follow up appointments, take medicines exactly as prescribed, and lean on support groups or online forums for tips from people in the same boat.
Bottom line: bone marrow disorders are serious but manageable with early detection, proper medical care, and everyday habits that boost your blood health. Stay curious, stay proactive, and don’t hesitate to ask your doctor any question that comes to mind.
The Role of Medication in Managing Bone Marrow Disorders
As a blogger, I recently explored the role of medication in managing bone marrow disorders. I discovered that medications play a crucial role in treating these disorders, such as anemia, leukemia, and myelodysplastic syndromes. Some of the most common medications include growth factors, immunosuppressive drugs, and chemotherapy, which help to stimulate blood cell production, reduce inflammation, and destroy cancer cells. Furthermore, medication also helps to manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients with bone marrow disorders. Overall, the proper use of medication is crucial for effective treatment and management of these complex health conditions.
Read More